CHAPTER 3: GETTING TO KNOW PLANTS
Have you ever observed the plants around you? Do you see how different they are? Some plants are huge and some are just tiny shrubs. Let us see the different parts of a plant
Have you ever observed the plants around you? Do you see how different they are? Some plants are huge and some are just tiny shrubs. Let us see the different parts of a plant
CLASSIFICATION OF PLANTS:
Plants can be classified into three categories based on their various characteristics:
1. Herbs: Plants with green and tender stems are called herbs. They are usually short and may not have many branches.
2. Shrubs: Some plants have the stem branching out near the base. The stem is hard but not very thick. Such plants are called shrubs.
3. Trees: Some plants are very tall and have hard and thick brown stem. The stems have
branches in the upper part, much above the ground. Such plants are called trees.
There are also creepers which are plants with weak stems that cannot stand upright and spread on the ground while those that take support on the neighbouring structures and climb up are called climbers.
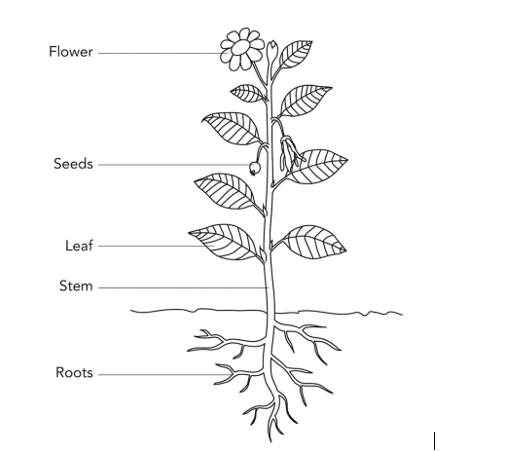
PARTS OF PLANT:
1. Stem: Stem conducts water. Minerals dissolved in water also move up in the stem, along with the water. The water and minerals go to leaves and other plant parts attached to the stem, through narrow tubes inside the stem.
2. Leaf: The part of a leaf by which it is attached to the stem is called petiole. The broad,
green part of the leaf is called lamina. The lines on the leaf are called veins. The thick vein in the middle is called the midrib. The design made by veins in a leaf is called the leaf venation. If this design is net-like on both sides of the midrib, the venation is called reticulate. But if the veins are parallel to one another, it is called parallel venation.
Plants can be classified into three categories based on their various characteristics:
1. Herbs: Plants with green and tender stems are called herbs. They are usually short and may not have many branches.
2. Shrubs: Some plants have the stem branching out near the base. The stem is hard but not very thick. Such plants are called shrubs.
3. Trees: Some plants are very tall and have hard and thick brown stem. The stems have
branches in the upper part, much above the ground. Such plants are called trees.
There are also creepers which are plants with weak stems that cannot stand upright and spread on the ground while those that take support on the neighbouring structures and climb up are called climbers.
PARTS OF PLANT:
1. Stem: Stem conducts water. Minerals dissolved in water also move up in the stem, along with the water. The water and minerals go to leaves and other plant parts attached to the stem, through narrow tubes inside the stem.
2. Leaf: The part of a leaf by which it is attached to the stem is called petiole. The broad,
green part of the leaf is called lamina. The lines on the leaf are called veins. The thick vein in the middle is called the midrib. The design made by veins in a leaf is called the leaf venation. If this design is net-like on both sides of the midrib, the venation is called reticulate. But if the veins are parallel to one another, it is called parallel venation.
The functions of leaves are transpiration and photosynthesis. Transpiration is a process by which water comes out of the leaves in the form of vapour. Photosynthesis is a process through which leaves prepare their food in the presence of sunlight and a green coloured substance present in them. Oxygen is given out in this process. The food ultimately gets stored in different parts of plant as starch.
3. Roots: Roots are the part of the plant that is under the soil. The roots help in holding the plant firmly in the soil. They are said to anchor the plant to the soil. There are two types of roots:
(i) Tap root: There is one main root and many small roots.
(ii) Fibrous root: There is no main root. All the roots are similar.
3. Roots: Roots are the part of the plant that is under the soil. The roots help in holding the plant firmly in the soil. They are said to anchor the plant to the soil. There are two types of roots:
(i) Tap root: There is one main root and many small roots.
(ii) Fibrous root: There is no main root. All the roots are similar.
4. Flower: A flower is the reproductive part of the plant. Let us see the different parts it has:
àOuter parts:
(i) Petals: The prominent parts on an open flower are called petals.
(ii) Sepals: The small leaf like structures are called sepals.
4. Flower: A flower is the reproductive part of the plant. Let us see the different parts it has:
àOuter parts:
(i) Petals: The prominent parts on an open flower are called petals.
(ii) Sepals: The small leaf like structures are called sepals.
- Inner parts:
(i) Stamen: Stamens consist of Anther and a stalk like structure- Filament.
(ii) Pistil: The innermost part of a flower is called pistil. The pistil also has stigma, style, ovary.
(iii) Ovary: It is the lowermost, swollen part of the pistil. It contains small bead-like structures called ovules.
The number of sepals, petals, stamens, etc. may be different in different flowers. In fact, sometimes, some parts may also be absent.